Home » Articles » New Use for Helium
A New Use for Helium
A hard drive sealed in helium has enormous performance advantages over the standard hard drive.

Helium hard drive: A hard drive running in a helium environment has many advantages over a hard drive running in air. Photo copyright iStockphoto / deepblue4you.
Why Helium?
Helium has the lowest density and lowest specific heat of all nonflammable substances. These two characteristics make helium the gas of choice for many specialized uses. Its primary use is as a coolant in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. That use has created a strong demand for a natural gas byproduct that can be produced in just a few parts of the world with unusual geologic conditions.
Now another use could begin to consume this rare gas even faster. Western Digital has produced the first computer hard drive sealed in a helium atmosphere. The drive was designed for use in data centers where hundreds or thousands of computers are operating.
Why helium? Helium has just 1/7 the density of air. This sealed helium drive produces less air turbulence, which in turn saves power consumption, produces less heat, produces fewer vibrations, makes less noise, allows greater drive capacity, and results in a much lower total cost of operation. The drives are expensive to manufacture, but that cost is recovered in energy savings and performance gains.
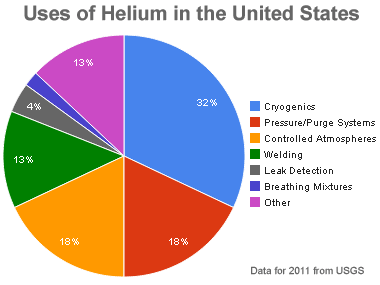
Uses of helium: Relative amounts of helium consumed by various uses in the United States. How will the consumption of helium for hard drives fit into this mix? Graph by Geology.com using data from USGS.
Lower Turbulence
Compared to air, helium's lower density allows the drive to spin with much less turbulence. The lower level of turbulence allows the motor to turn the drive with a power consumption savings of 23%. And, the lower level of turbulence allows seven platters to operate in a one-inch-high drive, instead of five. This increases the storage capacity of the drive by 50 percent - from 4 TB to 6 TB - and increases the storage capacity of a server and its weight per TB.
Less Noise
The lower level of air turbulence inside of the drive will reduce the amount of vibration produced by the spinning platters. The lower vibration level has been found to reduce the amount of noise produced by the drive by about 30%.
Less Heat
The lower turbulence within the drive means there is less friction produced between air molecules. This allows the drive to operate at a temperature that is about 4 degrees Celsius cooler within the drive. This means that the drive will shed less heat into the data center and lower the amount of air conditioning required - which results in another way to save power.
The Fugitive Gas Challenge
Producing a hard drive sealed in a helium environment was an enormous challenge. Why? Helium atoms are so small that they can seep through almost any material. Creating a case that will contain helium over a long period of time was the most difficult part of producing the drive - and the reason why helium drives did not go into use a long time ago.
The tightly-sealed case produces a few more advantages. Humidity, dust and other contaminants are kept out. This is expected to reduce drive failure rates and increase the average life expectancy of the helium drive.
The helium hard drive is an example of how using special materials creates special challenges but can result in exceptional savings.
An archived copy of the Western Digital (HGST) product announcement can be obtained here.
Author: Hobart M. King, Ph.D.
| More General Geology |
 |
Spectacular Fossils |
 |
What is the San Andreas Fault? |
 |
Bubbles in Amber |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
Fossils |
 |
Diamonds |
 |
Minerals |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
