Home » Geologic Hazards » Expansive Soil
Expansive Soil and Expansive Clay
The hidden force behind basement and foundation problems
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD

Building damage: Note displaced bricks and inward deflection of foundation. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Photo. Click to Enlarge.
What is an "Expansive Soil"?
Expansive soils contain minerals such as smectite clays that are capable of absorbing water. When they absorb water, they increase in volume. The more water they absorb, the more their volume increases. Expansions of ten percent or more are not uncommon. This change in volume can exert enough force on a building or other structure to cause damage.
Cracked foundations, floors, and basement walls are typical types of damage done by swelling soils. Damage to the upper floors of the building can occur when motion in the structure is significant.
| In a typical year in the United States, expansive soils cause a greater financial loss to property owners than earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and tornadoes combined. |
Expansive soils will also shrink when they dry out. This shrinkage can remove support from buildings or other structures and result in damaging subsidence. Fissures in the soil can also develop. These fissures can facilitate the deep penetration of water when moist conditions or runoff occurs. This cycle of shrinkage and swelling places repetitive stress on structures, and damage worsens over time.

Cracks in expansive soil: Desiccation cracks in soil caused by drying. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Photo. Click to Enlarge.
How Many Buildings are at Risk?
Expansive soils are present throughout the world and are known in every US state. Every year they cause billions of dollars in damage. The American Society of Civil Engineers estimates that 1/4 of all homes in the United States have some damage caused by expansive soils. In a typical year in the United States, they cause a greater financial loss to property owners than earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and tornadoes combined.
Even though expansive soils cause enormous amounts of damage, most people have never heard of them. This is because their damage is done slowly and cannot be attributed to a specific event. The damage done by expansive soils is then attributed to poor construction practices or a misconception that all buildings experience this type of damage as they age.
Homeowners Insurance and Expansive Soils
Damage to a home caused by expansive soils can be catastrophic for a homeowner. Why? Most homeowners insurance policies do not cover damage caused by expansive soils. The cost of repairs and mitigation can be extremely high - it sometimes exceeds the value of the home. In many cases the homeowner noticed the problem, didn’t realize its severity, didn’t realize that it was progressing, and the problem progressed to a point where repair didn’t make economic sense.
See our article: Homeowners Insurance and Geologic Hazards

Deflected basement wall: Inward deflection of a basement wall and pilasters. The plumb-bob reveals 9 inches of inward displacement. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Photo. Click to Enlarge.
Expandable, Shrink-Swell, Heavable Soils?
Expandable soils are referred to by many names. "Expandable soils," "expansive clays," "shrink-swell soils," and "heavable soils" are some of the many names used for these materials. The problem is so unfamiliar to the average homeowner that they don't know what to call it.
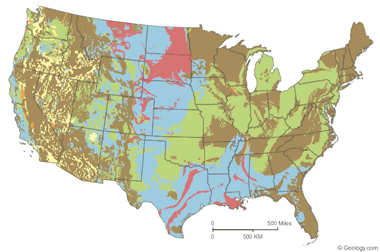
| Over 50 percent of these areas are underlain by soils with abundant clays of high swelling potential. | |
| Less than 50 percent of these areas are underlain by soils with clays of high swelling potential. | |
| Over 50 percent of these areas are underlain by soils with abundant clays of slight to moderate swelling potential. | |
| Less than 50 percent of these areas are underlain by soils with abundant clays of slight to moderate swelling potential. | |
| These areas are underlain by soils with little to no clays with swelling potential. | |
| Data insufficient to indicate the clay content or the swelling potential of soils. |
Expansive soils map: The map above is based upon "Swelling Clays Map of the Conterminous United States" by W. Olive, A. Chleborad, C. Frahme, J. Shlocker, R. Schneider and R. Schuster. It was published in 1989 as Map I-1940 in the USGS Miscellaneous Investigations Series. This map was generalized for display on the web by Bradley Cole of Geology.com using a base map licensed from MapResources. Click to Enlarge.
Land areas were assigned to map soil categories based upon the type of bedrock that exists beneath them as shown on a geologic map. In most areas, where soils are produced "in situ," this method of assignment was reasonable. However, some areas are underlain by soils which have been transported by wind, water or ice. The map soil categories would not apply for these locations.
Expansive Soils Map
The map on this page shows the generalized geographic distribution of soils that are known to have expandable clay minerals which can cause damage to foundations and structures. It also includes soils that have a clay mineral composition which can potentially cause damage.
| Expansive Soils Information on the Web |
|
Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Expansive Soil Damage? - Geology.com Expansive Soil And Foundation Cracks Video - Ask The Builder Expansive Soil and Rock - Colorado Geological Survey Understanding Soil Risks and Hazards - United States Department of Agriculture |
How to Interpret the Map
The map is meant to show general trends in the geographic distribution of expansive soils. It is not meant to be used as a property evaluation tool. It is useful for learning areas where expansive soils underlie a significant portion of the land and where expansive soils might be a localized problem.
All construction projects should include a soil analysis to identify the types of soil present and determine their expansive properties. Local occurrences of expansive soils can be found in all of the soil categories shown on this map.
Why Do These Soils Expand?
Soils are composed of a variety of materials, most of which do not expand in the presence of moisture. However, a number of clay minerals are expansive. These include: smectite, bentonite, montmorillonite, beidellite, vermiculite, attapulgite, nontronite, and chlorite. There are also some sulfate salts that will expand with changes in temperature.
When a soil contains a large amount of expansive minerals, it has the potential of significant expansion. When the soil contains very little expansive minerals, it has little expansive potential.
Changes in Moisture Content Trigger Damage
When expansive soils are present, they will generally not cause a problem if their water content remains constant. The situation where greatest damage occurs is when there are significant and repeated moisture content changes.
The Bottom Line
It is possible to build successfully and safely on expansive soils if stable moisture content can be maintained or if the building can be insulated from any soil volume change that might occur. The procedure for success is as follows:
 Testing to identify any problems Testing to identify any problems Design to minimize moisture content changes and insulate from soil volume changes Design to minimize moisture content changes and insulate from soil volume changes Build in a way that will not change the moisture conditions of the soil Build in a way that will not change the moisture conditions of the soil Maintain a constant moisture environment after construction Maintain a constant moisture environment after construction |
Expert assistance is usually needed to do these things successfully.
| More Geologic Hazards |
 |
Largest Hurricanes |
 |
Gifts That Rock |
 |
Storm Surge |
 |
World Record Lightning |
 |
Earthquakes |
 |
Landslides |
 |
Expansive Soil |
 |
Hurricane Names |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
