Home » General Geology » Water Dowsing
Dowsing as a Method of Finding Underground Water
Many people believe that dowsing is a valid method for finding groundwater.
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD, RPG

Figure 1: A person using a forked-stick dowsing rod in a field. The dowser walks through the field with the dowsing rod. When he walks over a location that has the potential of yielding water, the dowsing rod will rotate in his hands and point toward the ground. Many dowsers prefer forked sticks made from willow, peach, or witch hazel wood. Image copyright iStockphoto / Monika Wisniewska.
What Is Dowsing?
"Dowsing," "water witching," "divining," and "doodlebugging" are all names for the practice of locating groundwater by walking the surface of a property while holding a forked stick, a pair of L-shaped rods, a pendulum, or another tool that responds when the person moves above a location that will yield an adequate flow of water to a drilled well (see Figure 1).
People who practice dowsing believe that groundwater moves in subsurface seams, veins, or streams that must be intersected by the drill to produce an adequate flow of water. They believe that locations where this water is present are surrounded by forces that will produce a response in their tools. Forked sticks held in front of a dowser will be deflected toward the ground, a pair of L-shaped rods held lightly in the dowser's hands will cross one another, and a pendulum suspended on a string will deflect from vertical as the dowser moves over a good location.
Why Do Landowners Hire Dowsers?
Drilling a water well can cost thousands of dollars. It is a major investment that many landowners are hesitant to make without professional consultation. They want to be sure that the well is drilled in a location where it will produce water of adequate quantity and quality. This is why many people hire a dowser. They want to drill a successful well, close to their house, where the cost of installing water lines and an electrical conduit will be minimal and where a drilling rig can be easily driven.
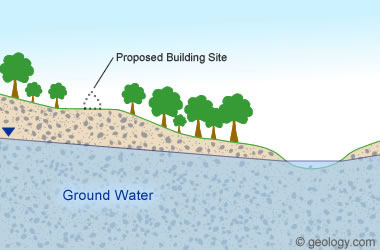
Figure 2: A cross-section of a building site above sedimentary materials. The blue line marks the subsurface location of the water table. Wells drilled throughout the area will penetrate the same materials and have a high probability of yielding water.
What Do Hydrogeologists Think of Dowsing?
Although some dowsers have a record of regularly producing good results, the United States Geological Survey reports that most geologists and hydrogeologists do not endorse the practice of dowsing [1]. The National Ground Water Association, in a position statement, "strongly opposes the use of water witches to locate groundwater on the grounds that controlled experimental evidence clearly indicates that the technique is totally without scientific merit" [2].

Figure 3: A drawing from De Re Metallica, by Georgius Agricola, published in 1556. It shows two workers using dowsing rods to locate subsurface ore minerals. Although Agricola used this illustration in his book and reported that the dowsing rod was being used to locate minerals, he rejected the practice and instead recommended trenching [5].
The Nature of Underground Water
Most fresh groundwater occurs in the pore spaces of sedimentary rocks and sediments. It has the ability to flow laterally through these pore spaces and establish a "water table" that is generally horizontal or slightly sloping (see Figure 2). If a landowner wants a well drilled within a hundred or so feet of a building site, almost any location selected will have similar potential for yielding water to a well. Why? Because the same types of rocks are usually present beneath that small area.
Locating and drilling into a good water supply can be difficult in areas underlain by igneous rocks such as granite and basalt. These rocks do not contain pore spaces through which water can flow. Instead, the water must move through very narrow fractures in the rock. A well must intersect enough of these tiny fractures to produce useful amounts of water. It can be very difficult to drill successful wells in some areas underlain by thick cavernous limestone. In these areas, wells that do not intersect a fracture or a cavern might not yield abundant water.
Regarding these igneous and limestone areas, geologists and hydrogeologists believe that there is no scientific basis for a dowser or a dowsing tool to have the ability to select a location where a drilled well will intersect subsurface fractures or small caverns.
 |
Other Types of Dowsing: Dowsing is not limited to finding water. Many dowsers believe the same methods can be used to locate oil, mineral deposits, buried utility lines, septic tanks, graves, lost jewelry, and other objects. Some believe that they can hold their tools over a map to locate objects below the ground at locations that are thousands of miles away. Image copyright iStockphoto / Noppadol_Anaporn. |
 |
Decide for Yourself: Marty Cain, a member of the American Society of Dowsers, has published a YouTube video titled "How to Find Water with Dowsing." In this video she demonstrates the use of L-rods and a pendulum for finding water. She also explains several methods of dowsing "on-site" and dowsing "at-a-distance" to find sources of pure potable water. |
How Do Hydrogeologists Locate Water?
Most successful water wells are drilled without the advice of a hydrogeologist. Local drilling companies often have the experience of drilling hundreds or thousands of wells in the areas where they operate. They have learned through this experience the parts of their service area where wells with adequate amounts of quality water are usually encountered. They also know areas where locating an adequate water supply can be challenging.
If a hydrogeologist is called to determine a suitable drilling site, he or she will start by examining a geologic map. These maps show the types of rocks that exist below the landowner’s property and their direction of dip. They also provide information about the different types of rock units that exist in the area. Some types of rocks are known to be good producers of water, whereas others will not hold or yield useful water.
The dip of the rock units and the topography of the area can be studied to identify the direction of groundwater flow, potential water recharge areas, springs, and discharge points. The depth of impermeable rock units can sometimes be determined, and these can serve as a lower limit for drilling. All this information allows the hydrogeologist to develop a three-dimensional model of the property that might define locations that are promising or those that should be avoided.
The hydrogeologist will also seek information about previous wells drilled in the local area. Most drillers maintain a file of the types of rocks penetrated and the amount of water produced for each well that they have drilled. This information is very useful in determining the probability of drilling success on a nearby property.
Hydrogeologists often examine aerial photos when siting a well in a challenging area. Aerial photos often reveal linear features that might indicate the presence of fracture zones in the bedrock. These areas often yield abundant water to wells.
Using the information described in the studies above, hydrogeologists base their recommendations on 1) the characteristics of the land; 2) characteristics of rocks beneath the site; 3) results from previous drilling; and, 4) known principles of groundwater movement. They believe that this type of information is more useful for siting a well than how a stick, a wire, or a pendulum responds to an unknown force [3] [4].
| REFERENCES |
|
[1] Water Dowsing: A general interest publication by the United States Geological Survey; 1988.
[2] Water Witching: A position paper by the National Ground Water Association; originally adopted in 1989; updated in 1992; reformatted in 2009; updated in 2016. [3] How Do Hydrologists Locate Groundwater?: Article on the United States Geological Survey website; last updated June 2018. [4] Ground Water in Fractured Hard Rock: A "Water Facts" publication of the California Department of Water Resources; April 1991. [5] De Re Metallica: Georgius Agricola, published posthumously in Germany in 1556. |
Conclusions
Many successful wells are drilled without the cost of a dowser or a hydrogeologist. The driller often has a lot of experience in the area being drilled and knows if the rocks in that area typically yield useful quantities of water.
When professional consultations are required or preferred, the landowner must make a decision. Should the project costing thousands of dollars be based upon scientific information about the rocks beneath a site, their water-yielding properties, and known principles of groundwater flow; or, should it be based upon a forked stick and an unexplainable force?
| More General Geology |
 |
Fossils |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Diamonds |
 |
Minerals |
 |
Divisions of Geologic Time |
 |
Land Below Sea Level |
 |
Gifts That Rock |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
