Home » Gemstones » Turritella Agate
Turritella Agate
Named "Turritella" in error decades ago. The correct name would be "Elimia Agate."
Author: Hobart M. King, PhD, GIA Graduate Gemologist

Turritella Agate / Elimia Agate: A close-up photo of a sawn surface of Turritella Agate showing numerous spiral-shaped snail shells. This type of view shows how the internal cavities of the shells and the voids between the shells have all been infilled with the translucent-to-transparent agate. This view is about two inches across.
What is Turritella Agate?
Turritella Agate is the popular name used for a brown, translucent to semi-transparent, fossiliferous agate found in the Green River Formation of Wyoming. It is very easy to recognize because it contains large fossil snails that stand out in a white-to-tan color that contrasts with the brownish agate.
This organic gem material was incorrectly named decades ago when the christener thought that the spectacular spiral-shaped gastropod (snail) fossils entombed within the stone were members of the marine Turritella genus. That was a mistake. Instead, the fossils are of the freshwater snail, Elimia tenera, a member of the Pleuroceridae family.
Before the correct name was realized and widely published, the gem material became quite popular and the name "Turritella" went wild in lapidary magazines, gem, mineral, and fossil books, catalogs, and exhibits. Today it is typically seen without corrective note in all of those sources, along with websites, online auctions, and computer software. Only a fraction of the people who have collected the material, cut it into cabochons, sold it, bought it, or worn it in jewelry have any knowledge that Elimia is a more appropriate name.
It is possible that the misnamed Turritella is the best-known fossil from the Green River Formation.
Table of Contents
 What is Turritella Agate? What is Turritella Agate? How did Turritella Agate Form? How did Turritella Agate Form? Turritella Agate: The Gem Material Turritella Agate: The Gem Material What About Elimia tenera? What About Elimia tenera? |

Turritella Agate cabochon: A cabochon cut from Turritella Agate that features one of the spiral-shaped snail shells. This cab is about 1 1/2 by 1 inch in size.
How did Turritella Agate Form?
About 50 million years ago, during the Eocene epoch, the young Rocky Mountains were almost finished growing, and the landscape of what is now parts of Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming consisted of rugged mountains separated by broad intermountain basins. Rains falling on the slopes of these mountains ran off of the land and collected into streams that carried sand, silt, mud, and dissolved materials down into the lakes that occupied the intermountain basins. Over time, these sediments began filling the lakes, and many types of fossils were preserved within them.
Abundant plants and algae grew on the margins of these lakes, providing a perfect habitat and food source for Elimia tenera, the freshwater snail. When the snails died, their shells sank to the bottom of the lake. The snails were so prolific that entire lenses of sediment were composed almost entirely of their shells.
After these layers were buried, groundwater moved through the sediments. Small amounts of dissolved microcrystalline silica in the groundwater began to precipitate, possibly in the form of a gel, within the cavities of the snail shells and the empty spaces between them. Over time, the entire mass of fossils was silicified, forming the brown fossiliferous agate (also known as chalcedony) that we know today as Turritella agate.
The Green River Formation is one of the best-known rock units in the world for its fossils. Some geologists call it a "lagerstätte," a name given to a rock unit that is exceptionally rich in fossils. Spectacular fish, plant, insect, and animal fossils have been found in the Green River Formation.

Turritella slab: A slab of Turritella Agate about six inches in width and 3/8 inch thick. Slabs like this are used to cut cabochons. The lapidary selects a nice scene in the slab, saws a rough outline, and grinds the material into a cab.
Turritella Agate: The Gem Material
For at least the past fifty years, Turritella agate has been prized as a unique and beautiful gem material. When it is completely silicified, it can be sawn into slabs that are polished and used for bookends, desk sets, clock faces, and other lapidary craft items.
Many lapidaries mark ovals, circles, squares and other shapes on the slabs and cut them into cabochons. These make great pendants, belt buckles, bolos, ring stones, and earrings. Scraps and pieces too small to slab or make other items with can be placed in a rock tumbler to produce some of the most interesting tumbled stones.
People who see these beautiful projects marvel that so many spectacular fossils are preserved in the rock. They are also surprised by the cross-sections of the fossils that are visible in great detail on the slabs, cabs, and tumbled stones. Turritella is one of the most fascinating gem materials and a lesson in snail anatomy.

Looking Closely at Turritella: The closer you look at Turritella, the more fossils you find. We looked at a Turritella cabochon with a microscope and saw tiny ostracod fossils in the spirals of the gastropod fossils. See our Looking Into the Mysteries of Gems article for more information and other photos of gems through a microscope. Enlarge image.
The rock material that contains the fossil snails ranges from a shale to a sandstone. Only a small portion of this rock unit has been silicified into the dense agate that is needed to serve as a gem material. The rest of the rock unit is only somewhat silicified, or unsilicified.
When purchasing or collecting Turritella agate for lapidary work, you must carefully inspect it and make sure that it is fully silicified and that the fossils are firmly cemented into the rock. Some of the vendors who sell it do not know the qualities that are needed for lapidary work. Incompletely silicified material is a waste of time and money. It is frustrating to cut, yields a low-quality product, and doesn't even make nice tumbled stones.
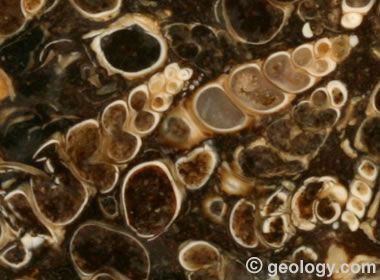
Turritella Agate rough: Another close-up photo of Turritella Agate. The width of this view is about two inches.
What About Elimia tenera?
If you go into a rock shop or a gem, mineral, and fossil show and ask for "Elimia Agate," a lot of people will say that they have never heard of it. But, if you ask for Turritella, almost everyone around you will know what it is. The incorrect name is that well-entrenched in the lapidary trade.
If you want to learn more about Elimia tenera and the best name for Turritella Agate, we recommend a visit to the Paleontological Research Institution - people who know what they are talking about when it comes to fossils. Their article on Turritella Agate was authored by Dr. Warren D. Allmon, Director of the Institution.
| More Gemstones |
 |
Birthstones |
 |
Diamond |
 |
Blue Gemstones |
 |
100+ Gems |
 |
Green Gemstones |
 |
Mined in America |
 |
Ruby and Sapphire |
 |
Tumbled Stones |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
