Home » Geology Articles » What Is Geology? - What Does a Geologist Do?
What Is Geology? - What Does a Geologist Do?
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD, RPG
The Relevance of Geology: A student / faculty video produced by Union College Geosciences Department.
Definition of Geology:
Geology is the study of the Earth, the materials of which it is made, the structure of those materials, and the processes acting upon them. It includes the study of organisms that have inhabited our planet. An important part of geology is the study of how Earth's materials, structures, processes and organisms have changed over time.
Geoscience Careers: Why a career in the Earth sciences is important. Geological Society of America.
What Does a Geologist Do?
Geologists work to understand the history of our planet. The better they can understand Earth’s history, the better they can foresee how events and processes of the past might influence the future. Here are some examples:
Geologists study Earth processes: Many processes such as landslides, earthquakes, floods, and volcanic eruptions can be hazardous to people. Geologists work to understand these processes well enough to avoid building important structures where they might be damaged. If geologists can prepare maps of areas that have flooded in the past, they can prepare maps of areas that might be flooded in the future. These maps can be used to guide the development of communities and determine where flood protection or flood insurance is needed.
Geologists study Earth materials: People use Earth materials every day. They use oil that is produced from wells, metals that are produced from mines, and water that has been drawn from streams or from underground. Geologists conduct studies that locate rocks that contain important metals, plan the mines that produce them and the methods used to remove the metals from the rocks. They do similar work to locate and produce oil, natural gas, and groundwater.
Geologists study Earth history: Today we are concerned about climate change. Many geologists are working to learn about the past climates of Earth and how they have changed across time. This historical geology news information is valuable to understand how our current climate is changing and what the results might be.
| Volcanic Hazards Map |
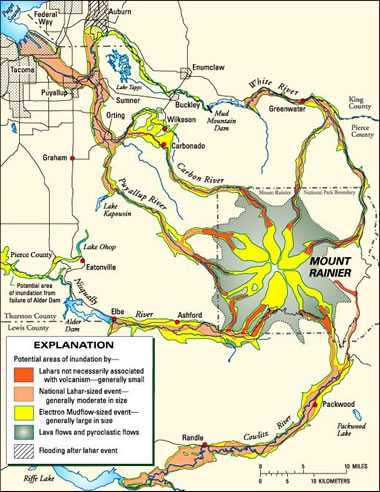
Volcanic Hazards Map: Geologists prepared this volcanic hazards map to communicate the location of hazardous areas to citizens, government agencies, and businesses. To prepare a map like this requires an understanding of volcanoes, an ability to recognize volcanic deposits in the field, an ability to prepare a map, and an ability to communicate. All geological tasks require a diversity of skills. This is why students who are interested in geology are encouraged to do well in all of their courses and to seek advanced training in Earth science, chemistry, physics, math, computers, and communication skills. USGS image. View larger map.
Geology as a Career
Geology can be a very interesting and rewarding career. The minimum training required is a four-year college degree in geology. Pre-college students who are interested in becoming geologists should take a full curriculum of college preparatory courses, especially those in math, science, and writing. Courses related to computers, geography and communication are also valuable.
Geologists work in a variety of settings. These include: natural resource companies, environmental consulting companies, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and universities. Many geologists do field work at least part of the time. Others spend their time in laboratories, classrooms or offices. All geologists prepare reports, do calculations and use computers.
Although a bachelor's degree is required for entry-level employment, many geologists earn master's and/or doctorate degrees. The advanced degrees provide a higher level of training, often in a geology specialty area such as paleontology, mineralogy, hydrology, or volcanology. Advanced degrees will often qualify the geologist for supervisory positions, research assignments, or teaching positions at the university level. These are some of the most sought-after jobs in the field of geology.
Employment opportunities for geologists are very good. Most geology graduates with a strong academic background and good grades have no trouble finding employment if they are willing to move to a location where work is available.
More Information
Graduate Study in Geology
Geology Assistantships
Geology Job Information
Geologist Starting Salaries
Employment Outlook
Over the next several years, the number of geology job openings is expected to exceed the number of students graduating from university geology programs. Starting salaries for geologists have recently ranged from $50,000 to $100,000 per year.
How Can You Become a Geologist?
If you are a pre-college student, you can prepare to become a geologist by doing well in all of your courses. Science courses are especially important, but math, writing, and other disciplines are used by every geologist during every working day.
If you are considering college or graduate school, there are many universities that offer courses or programs in geology. Visit the website of a school that offers a geology degree, get in touch with the geology department, let them know you are interested, and make arrangements to visit the campus. Don't be hesitant. Good schools and professors want to be contacted by interested students.
| More General Geology |
 |
Diamonds from Coal? |
 |
What is a Geyser? |
 |
What is the San Andreas Fault? |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
The Doorway to Hell |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Gifts That Rock |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
