Home » Oil and Gas » Uses of Natural Gas
Uses of Natural Gas
Natural gas is an important fuel and a raw material in manufacturing.
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD
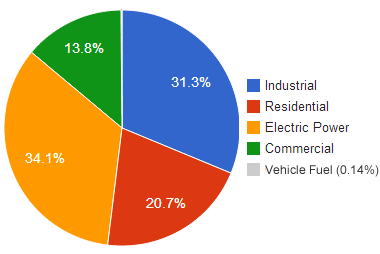
End Use of Natural Gas in the United States: Electric power generation, industry, residences and commercial buildings were the major natural gas consuming sectors in the United States during calendar year 2013. Only 0.14% went to use as a vehicle fuel. Image by Geology.com using data from the United States Energy Information Administration.
Natural Gas: A Fuel and a Raw Material
Natural gas is used in an amazing number of ways. Although it is widely seen as a cooking and heating fuel in most U.S. households, natural gas has many other energy and raw material uses that are a surprise to most people who learn about them.
In the United States, most natural gas is burned as a fuel. In 2012 about 30% of the energy consumed across the nation was obtained from natural gas [1]. It was used to generate electricity, heat buildings, fuel vehicles, heat water, bake foods, power industrial furnaces, and even run air conditioners!
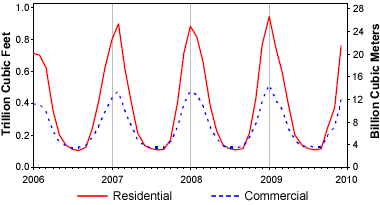
Natural gas consumption by residential and commercial customers: Residential and commercial demand for natural gas is highest in the winter when people burn gas to heat their homes and businesses. Since few people cool their home or business in summer with natural gas air conditioners, the summer demand is much lower. Image by U.S. Energy Information Administration.
22 Trillion Cubic Feet
During 2009 the United States consumed about 22.8 trillion cubic feet of natural gas. That's enough gas to fill a room with a footprint the size of Pennsylvania and about 18 feet high. Most of that gas was delivered to nearly 70 million homes and places of business through more than a million miles of natural gas pipelines [2].
Uses of Natural Gas in US Homes
Over one-half of the homes in the United States are supplied with natural gas. About 21% of the natural gas consumed in the United States during 2013 went to homes [1]. This gas is delivered to homes through pipelines or in tanks as CNG (compressed natural gas). Most of the natural gas consumed in homes is used for space heating and water heating. It is also used in stoves, ovens, clothes dryers, lighting fixtures and other appliances.

Surprising Uses Of Natural Gas: Natural gas is used to manufacture a wide variety of products. The fertilizer being spread in the top left image might have been made with ammonia produced from natural gas; the plastic parts of the spreader and the operator's clothing were most likely produced with the help of natural gas as an ingredient or as a fuel in the factory. Most bricks and cement are produced using natural gas as a heat source. Many pharmaceuticals and plastic bottles are made with natural gas as an ingredient. Cereal and fruits are often baked or dried using natural gas as a heat source. Images copyright iStockphoto and (clockwise) Bill Grove, John Leung, Kristine Slipson, and Amanda Rohde.
Uses of Natural Gas in Commercial Buildings
In 2013 about 14% of the natural gas consumed in the United States went to commercial buildings. The use of natural gas in commercial buildings is similar to its use in residences. It is used mainly for space heating, water heating and sometimes for air conditioning.
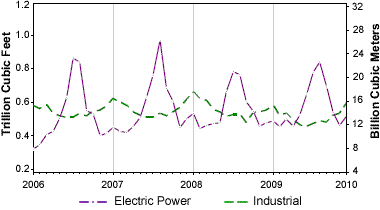
Natural gas demand by electric power and industrial customers: Demand for natural gas by the electric power industry in the United States peaks in the summer when homes and businesses are using air conditioning. Since very few homes and businesses have natural gas air conditioners, the demand goes to electricity. Image by U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Electric Power Generation
The electric power industry was the largest consumer of natural gas in the United States during 2013. About 34% of natural gas consumption was used to make electricity.
Of the three fossil fuels used for electric power generation (coal, oil, natural gas), natural gas emits the least carbon dioxide per unit of energy produced. It emits 30% less carbon dioxide than burning oil and 45% less carbon dioxide than burning coal. Burning natural gas also releases lower amounts of nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulates and mercury when compared to coal and oil [3].
As the United States becomes more concerned about climate change, carbon dioxide emissions, and air quality, the use of natural gas for electricity generation is expected to increase.
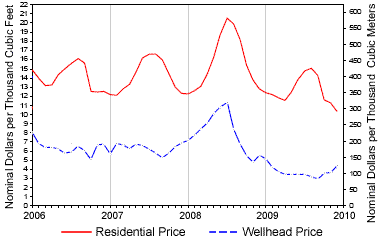
Natural gas price graph: Natural gas prices fluctuate over time. Wellhead prices are determined by supply, demand, and general economic conditions. Prices to consumers are determined by similar factors. Image by U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Industrial Uses of Natural Gas
Natural gas is used in a wide variety of manufacturing processes. About 31% of the 2013 consumption of natural gas in the United States was by industry. Natural gas is used as both a raw material and as a source of heat.
Natural gas is an ingredient used to make fertilizer, antifreeze, plastics, pharmaceuticals and fabrics. It is also used to manufacture a wide range of chemicals such as ammonia, methanol, butane, ethane, propane, and acetic acid.
Many manufacturing processes require heat to melt, dry, bake, or glaze a product. Natural gas is used as a heat source in making glass, steel, cement, bricks, ceramics, tile, paper, food products and many other commodities. Natural gas is also used at many industrial facilities for incineration.
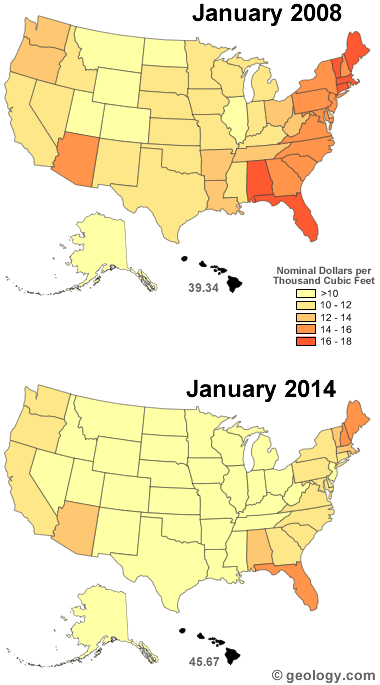
Natural gas price map: The price of natural gas is not uniform across the United States. Instead, the price is determined by supply, demand, proximity to supply, regulatory environments and the cost of natural gas that is flowing in the local distribution system. Historically, people along the east coast have paid some of the highest prices. This may change as new unconventional resources such as the Marcellus Shale are developed and as more LNG arrives from low-cost producers. Image by Geology.com using natural gas price data for calendar year 2008 from the United States Energy Information Administration.
Oil & Gas and Pipeline Industry Use
Companies that produce and transport natural gas are also consumers. Transporting natural gas through pipelines requires compression stations to keep the gas pressurized and flowing through the pipeline. Many of these compression stations use natural gas as a fuel. Many oil refineries use natural gas for heating and power generation.

Natural Gas Fleet Studies: The United States government has done many cooperative studies with businesses, local governments and public agencies related to the use of natural gas as a fleet vehicle fuel. The results of these studies have overwhelmingly favored natural gas. Summaries of these studies and many full reports can be downloaded from the U.S. Department of Energy website [5].
Natural Gas as a Vehicle Fuel
Natural gas has an enormous potential for increased use as a vehicle fuel. The main barriers to this have been the short range of the vehicles, limited refueling options, and slow refueling times. However, over the past few years refueling station prices have dropped to just a few hundred dollars, and these can be placed in residences where the vehicles can be refueled overnight or between trips.
Since about half of all residences in the United States are supplied with natural gas, the potential to increase the number of natural gas vehicles on the road is very high. In addition, the discovery of natural gas in shale deposits around the country has increased the availability of gas and decreased the price.
Natural gas has significant advantages over gasoline and diesel fuel. Natural gas vehicles emit 60-90% less smog-producing pollutants and 30-40% less greenhouse gas emissions. It also costs less per mile to operate a natural gas vehicle compared to a gasoline or diesel vehicle [4]. And, natural gas is produced locally instead of imported.
| References |
|
[1] What is U.S. electricity generation by energy source? United States Energy Information Administration. [2] Statistics from the Natural Gas Supply Association (2013), NGSA.org. [3] Get the Facts on Natural Gas for Electricity: PDF by the Natural Gas Supply Association, March 2017. [4] Natural Gas Vehicles: United States Department of Energy (2010), FuelEconomy.gov. [5] Alternative Fuels Data Center: United States Department of Energy. |
| More Oil |
 |
The Doorway to Hell |
 |
Oil Sands |
 |
Shale Gas Resources |
 |
Gifts That Rock |
 |
Horizontal Drilling |
 |
Oil and Gas Rights |
 |
Natural Gas Prices |
 |
Oil Shale |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
