
Satellite Image of Lake Baikal: Image by Geology.com using NASA Landsat data.
The World's Deepest Lake
Lake Baikal in southern Russia is the world's deepest lake. It is an estimated 5,387 feet deep (1,642 meters), and its bottom is approximately 3,893 feet (1,187 meters) below sea level. Lake Baikal is also the world's largest freshwater lake in terms of volume.
It is difficult to comprehend how a lake in the middle of the Asia could have a bottom that is nearly 4,000 feet below sea level. It is impossible for erosion to cut a channel that deep in the middle of a continent.
Lake Baikal is so deep because it is located in an active continental rift zone. The rift zone is widening at a rate of about 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) per year. As the rift grows wider, it also grows deeper through subsidence. So, Lake Baikal could grow wider and deeper in the future.
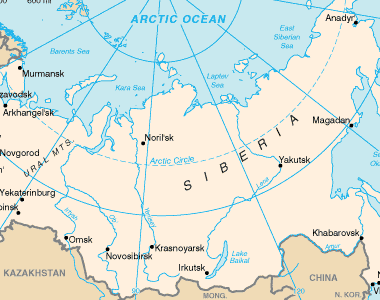
Lake Baikal map: Lake Baikal is located in southern Siberia near the city if Irkutsk. Map from the CIA Factbook.

Crater Lake: Panorama view of Crater Lake showing the steep crater wall that surrounds the lake and Wizard Island, a small volcano within the crater. Photo copyright iStockphoto / ziggymaj.
Deepest Lake in the United States:
The deepest lake in the United States is Crater Lake, a volcanic crater in southern Oregon. Its deepest measured depth is 1,949 feet (594 meters). It is the ninth-deepest lake in the world.
It is an amazing lake because no rivers flow into it or out of it. The water level in the lake is a balance between rainfall, groundwater flow and evaporation.
The lake is a volcanic crater that formed about 7600 years ago in the aftermath of one of the largest volcanic eruptions in recent geologic history. The explosive eruption ejected about 150 cubic kilometers of material, then the volcano collapsed into the empty magma chamber below to form a deep basin known as a caldera.
Deepest Lakes in the World | ||
| Baikal | Siberia, Russia | 5,387 ft (1,642 m) |
| Tanganyika | Tanzania, D.R. Congo & Zambia | 4,823 ft (1,470 m) |
| Caspian Sea | Iran & Russia | 3,363 ft (1025 m) |
| Vostok | Antarctica | 2,950 ft (900 m) minimums |
| O'Higgins-San Martin | Chile & Argentina | 2,742 ft (836 m) |
| Nyasa | Mozambique, Tanzania & Malawi | 2,316 ft (706 m) |
| Issyk Kul | Kyrgyzstan | 2,192 ft (668 m) |
| Great Slave | Northwest Territories, Canada | 2,015 ft (614 m) |
| Crater Lake | Oregon, U.S.A. | 1,949 ft (594 m) |
| Matano | Indonesia | 1,936 ft (590 m) |
| General Carrera | Chile & Argentina | 1,923 ft (586 m) |
| Hornindalsvatnet | Norway | 1,686 ft (514 m) |
| Quesnel | Canada | 1,660 ft (506 m) |
| Toba | Indonesia | 1,657 ft (505 m) |
| Sarez | Tajikistan | 1,657 ft (505 m) |
| Tahoe | California & Nevada, U.S.A. | 1,644 ft (501 m) |
| Argentino | Argentina | 1,640 ft (500 m) |
| Kivu | D.R. Congo & Rwanda | 1,575 ft (480 m) |
| Mjøsa | Norway | 1,535 ft (468 m) |
| Lake Chelan | Washington, U.S.A. | 1,486 ft (453 m) |
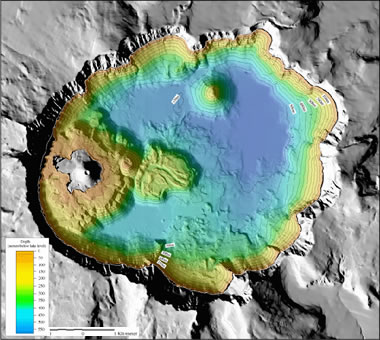
Crater Lake bathymetry: Bathymetry image of Crater Lake by USGS. The deepest areas are in the northeast portion of the lake. Enlarge map.
| Information Sources |
|
[1] Crater Lake: Summary on the USGS Volcano Hazards Program website. Last accessed September 2022.
[2] Facts about Crater Lake: Article on the Oregon Explorer Natural Resources Digital Library website, a collaboration of Oregon State University Libraries & Press and the Institute for Natural Resources. Last accessed September 2022. [3] Morphometric Data for Lake Baikal: The INTAS Project 99-1669 Team, October 2002. Marc DeBatist of Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium. Last accessed September 2022. |
Actual Lake Depths Will Vary
It is worth noting that estimated lake depths are just that - estimates. In fact, they are estimates of depths that change over time!
Searching online, a person may find several different depths listed for the same lake. Why is this?
The recorded depth of a lake may vary over time, depending on multiple factors.
Crater Lake, for example, does not have any streams or rivers flowing into or out of the lake. The water level is relatively constant because, remarkably, the amount of water coming into the lake (via rainfall and snowfall) generally equals the amount of water going out of the lake (via evaporation and seepage).
Since the depth of Crater Lake is directly influenced by the climate, it is easy to imagine how the water level would drop in a year of drought, or how the lake would become deeper in a year of record precipitation. These ideas can be applied to lakes fed and drained by rivers as well.
Another example of how the depth of a lake can change is with Lake Baikal, which is located over a continental rift. The rift is slowly getting wider and deeper each year, which means that the size of the lake is changing, too.
In addition to our planet changing over time, methods of measuring also change. Back in 1886, the depth of Crater Lake was estimated to be 608 meters - measured using a piano wire and lead weight. In 1959, the maximum depth was reported to be 589 meters with sonar measurement. And in July of 2000, 594 meters was the depth reached by a multibeam survey.
Three different depths were recorded at three different points in time with three different methods of measurement. Which is correct? They could all be accurate, or, none of them may be exactly right. There's no way to know with 100% certainty.
That is why it's important to keep in mind that these statistics are simply estimates, and the actual measurements are constantly changing, ever so slightly, even from one day to the next.
| More Earth Extremes |
 |
The World*s Largest Highly Acidic Lake |
 |
The Tallest Waterfall in the U.S. |
 |
The Most Explosive Eruption |
 |
Largest Volcano - |
 |
Angel Falls |
 |
Deepest Lake in the World |
 |
Bathyscaphe Trieste |
 |
World Record Lightning |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
