Coquina
A porous limestone composed almost entirely of fossil debris.
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD

Coquina: Coquina collected in Florida. This specimen measures approximately 9 centimeters across. Public Domain photo by Mark A. Wilson of the Department of Geology, The College of Wooster. Click to enlarge.
What Is Coquina?
Coquina is a sedimentary rock composed almost entirely of sand-size fossil debris. The fossils are usually mollusk or gastropod shells and shell fragments. Brachiopod, trilobite, coral, ostracod and other invertebrate shell debris is present in many coquinas. The fossil debris of coquina is composed of calcium carbonate, making coquina a variety of limestone.
Coquina contains very little silt or clay-size particles, and its fossil fragments are lightly cemented together. This makes it an extremely porous rock that can serve as an aquifer for community and private water supplies. It can also serve as a reservoir for oil and natural gas. Coquina is sometimes used as a construction material, but only where other materials of greater physical strength and durability are not available.
Table of Contents
 What is Coquina? What is Coquina? Where Does Coquina Form? Where Does Coquina Form? Rocks Related to Coquina Rocks Related to Coquina Mineral and Chemical Composition Mineral and Chemical Composition Uses of Coquina Uses of Coquina |

Coquina Outcrop: This outcrop of coquina is located in Washington Oaks Gardens State Park near Palm Coast, Florida. Creative Commons image by Ebyabe. Click to enlarge.
Where Does Coquina Form?
Most coquina forms in shallow coastal waters where a steady and abundant supply of sand-size fossil debris is delivered by wave action and currents. The waves and currents must be strong enough to completely remove clay and silt-size particles, but not so strong that the accumulation of sand-size fossil debris is eroded.
Most coquina-forming sediments are found in tropical or subtropical marine waters because that is where an abundant supply of fossil debris is most likely to be produced. They usually form along ocean beaches, barrier islands, shallow offshore bars, or tidal channels. In these depositional environments, the rock unit may develop sedimentary structures that include: bedding, cross-bedding, ripple marks, etc. A few coquina deposits are known from freshwater environments that include lakeshores and river channels.
Significant deposits of coquina are found along the coasts of Florida and North Carolina. They also occur along the coasts of Australia, Brazil, Mexico and the United Kingdom.
After deposition, calcium carbonate usually precipitates within the sediment. This can be in the form of a cement that binds the fossil debris together. This “cementation” is the essential step that transforms a sediment into a sedimentary rock.
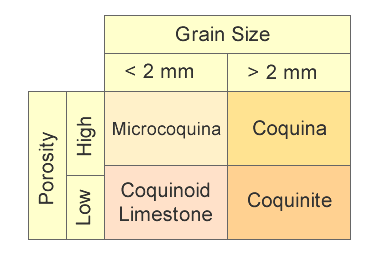
Coquina-Related Rocks: This chart shows the grain size and porosity of rocks that are related to coquina.
Rocks Related to Coquina
On the basis of grain size and matrix characteristics, three types of sedimentary rocks related to coquina can be distinguished: coquinite, microcoquina and coquinoid limestone. These are summarized in the accompanying classification chart and in the descriptions below:
 Coquinite is similar to coquina; however, the shell debris is more firmly cemented together. Coquinite is similar to coquina; however, the shell debris is more firmly cemented together. Microcoquina is also similar to coquina, but the shell particles are much smaller, under one millimeter in size. Microcoquina is also similar to coquina, but the shell particles are much smaller, under one millimeter in size. Coquinoid limestone is similar to coquina, but the spaces between the shell debris are occupied by fine-grained carbonate material. Coquinoid limestone is similar to coquina, but the spaces between the shell debris are occupied by fine-grained carbonate material. |
Mineral and Chemical Composition
Coquina and related sedimentary rocks are composed mainly of calcium carbonate. When the deposits are geologically young, much of the calcium carbonate is in the form of aragonite, as this is what mollusks and gastropods use to build their shells. However, during diagenesis the aragonite transforms into calcite.

Castillo de San Marcos is a star-shaped fort with thick walls built from blocks of coquina. Built in 1672, it survived attacks and sieges because of the ability of the walls to absorb cannonballs instead of breaking and crumbling into fragments. The fort still stands today and is an example of how a building material that is normally rejected can be superior for certain types of use. Image copyright iStockphoto / felixmizioznikov. Click to enlarge.
Uses of Coquina
Coquina has several uses. As a subsurface rock unit with a high porosity and permeability, coquina can serve as a groundwater aquifer or as a reservoir rock for oil and natural gas. These are the most significant economic uses of coquina.
Crushed stone made from coquina has been used in the construction of unpaved roads. It drains well; however, the weight of traffic gradually crushes the rock, requiring constant replenishment. Crushed coquina has also been used as a base material in many construction projects where abrasion resistance and ability to bear weight were not important.
Blocks of coquina have been used to construct walls, small buildings, and monuments. In these uses coquina can last for decades but eventually crumbles and fails. This failure can be delayed if the rock is sealed by plastering or parging.
As a construction material, coquina usually does not meet durability specifications. The rock has a high porosity, and the grains are poorly cemented together. That gives it a low compressive strength and a low abrasion resistance. These usually disqualify coquina for use as a building stone and as a construction aggregate.
One interesting exception to this is in the performance of the coquina used to construct Castillo de San Marcos, a Spanish Fort built in 1672 on the western shore of Matanzas Bay at St. Augustine, Florida. When English ships attempted to take the fort by siege in 1702, their cannonballs embedded themselves into the thick blocks of coquina instead of breaking them in a shower of deadly fragments. This property of the coquina enabled the fort to resist the attack of 1702, another attack in 1740, and the star-shaped fort still stands today.
| More Rocks |
 |
Tumbled Stones |
 |
Fossils |
 |
Geodes |
 |
The Rock Used to Make Beer |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Difficult Rocks |
 |
Fluorescent Minerals |
 |
Sliding Rocks on Racetrack Playa |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
