Home » Rocks » Igneous Rocks » Gabbro
Gabbro
What Is Gabbro, What Minerals Are In Gabbro, and What Is It Used For?
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD

Gabbro is a dark-colored coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock. The specimen shown above is about two inches (five centimeters) across.
What is Gabbro?
Gabbro is a coarse-grained, dark-colored, intrusive igneous rock. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the minerals plagioclase and augite. It is the most abundant rock in the deep oceanic crust. Gabbro has a variety of uses in the construction industry. It is used for everything from crushed stone base materials at construction sites to polished stone counter tops and floor tiles.
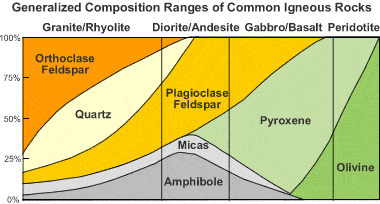
Igneous rock composition chart: A chart that illustrates the generalized mineral composition of igneous rocks. By studying this chart, you can see that gabbros and basalts are composed mainly of plagioclase feldspar, micas, amphiboles, and olivine.
What Minerals are in Gabbro?
Gabbro is composed mainly of calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar (usually labradorite or bytownite) and pyroxenes (usually augite). Minor amounts of olivine might also be present in the rock. (See composition chart on this page.)
This mineral composition usually gives gabbro a black to very dark green color. A minor amount of light-colored mineral grains may also be present. Unlike many other igneous rocks, gabbro usually contains very little quartz. You can see a close-up view of gabbro toward the bottom of this page.
Gabbro and Basalt are Related
Gabbros are equivalent in composition to basalts. The difference between the two rock types is their grain size. Basalts are extrusive igneous rocks that cool quickly and have fine-grained crystals. Gabbros are intrusive igneous rocks that cool slowly and have coarse-grained crystals.
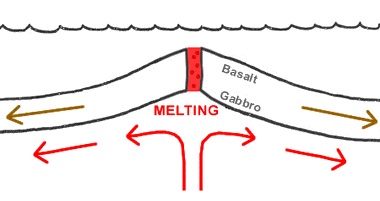
Divergent boundary: In the oceanic crust, basalt forms near the surface at a divergent boundary, but gabbro forms at depth from slow crystallization. Learn about teaching plate tectonics.
Gabbro in Oceanic Crust
It is often stated that Earth's oceanic crust is made up of basalt. The word "basalt" is used because the rocks of the oceanic crust have a "basaltic" composition. However, only a thin surface veneer of oceanic crust is basalt. The deeper rocks of the oceanic crust are generally coarser-grained gabbro. Basalt occurs at the surface of the crust because the rocks there have cooled quickly. At greater depth the cooling rate is slower, and large crystals have time to develop. (See illustration.)

Black granite: A view of polished gabbro (labradorite). Polished gabbro is sold under the name "black granite" and is used for cemetery markers, floor tile, kitchen counter tops, facing stone, and other dimension stone uses.
Gabbro in Continental Crust
On the continents, gabbro can be found within thick lava flows of basaltic composition, where slow cooling allows large crystals to form. Gabbro will also be present in the deep plutons that form when magma chambers that feed basaltic eruptions crystallize.
Large volumes of gabbro are present beneath extensive flood basalts such as the Columbia River flood basalts of Washington and Oregon and the Deccan Traps of India.

Close-up view of gabbro: Magnified view of the gabbro shown in the photograph at the top of the page. The area shown in this image is about 1/2 inch across.
Uses of Gabbro
Gabbro can be polished to a brilliant black luster. Brightly polished gabbro is used to make cemetery markers, kitchen counter tops, floor tiles, facing stone, and other dimension stone products. It is a highly desirable rock that stands up to weathering and wear.
In the dimension stone industry, gabbro is sold under the name "black granite." Gabbro is also used to make a number of rough-cut products such as curbing, ashlars, paving stones, and other products.
The most common use of gabbro is as a crushed stone or aggregate. Crushed gabbro is used as a base material in construction projects, as a crushed stone for road construction, as railroad ballast, and anywhere that a durable crushed stone is needed as fill.

Rock & Mineral Kits: Get a rock, mineral, or fossil kit to learn more about Earth materials. The best way to learn about rocks is to have specimens available for testing and examination.
Gabbro as an Ore
Gabbro sometimes contains economic amounts of some relatively rare metals. Gabbros containing significant amounts of the mineral ilmenite are mined for their titanium content. Other gabbros are mined to yield nickel, chromium, or platinum.
| More Rocks |
 |
Tumbled Stones |
 |
Fossils |
 |
Geodes |
 |
The Rock Used to Make Beer |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Difficult Rocks |
 |
Fluorescent Minerals |
 |
Sliding Rocks on Racetrack Playa |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
