Silver
The soft, white, native metallic element with a diversity of uses.
Article by: Hobart M. King, PhD

Silver crystals: Crystals of native silver on calcite from the New Nevada Mine, Batopilas, Chihuahua, Mexico. Specimen is approximately 11 x 7 x 6 centimeters in size. Specimen and photo by Arkenstone / www.iRocks.com.
What is Silver?
Silver is a soft, white metal that usually occurs in nature in one of four forms: 1) as a native element; 2) as a primary constituent in silver minerals; 3) as a natural alloy with other metals; and, 4) as a trace to minor constituent in the ores of other metals. Most of the silver produced today is a product of the fourth type of occurrence.
Silver is known as a "precious metal" because it is rare and because it has a high economic value. It is valuable because it has a number of physical properties that make it the best possible metal for many different uses.
Silver has an electrical and thermal conductance that is higher than any other metal. It has a higher reflectivity at most temperatures than any other metal. It has an attractive color and luster that resist tarnish and make the metal desirable in jewelry, coins, tableware, and many other objects.
These are just a few of silver's important properties. When performance is more important than price, silver is often the material of choice.

Silver wire: A specimen of wire silver with a heavy tarnish of acanthite on a calcite matrix. Specimen is approximately 6 x 4 x 3 centimeters in size. Specimen and photo by Arkenstone / www.iRocks.com.
Physical Properties of Silver |
|
| Chemical Classification | Native element |
| Color | Silvery white |
| Streak | Silvery white |
| Luster | Metallic |
| Diaphaneity | Opaque |
| Cleavage | None |
| Mohs Hardness | 2.5 to 3 |
| Specific Gravity | 10.0 to 11.0 |
| Diagnostic Properties | Color, specific gravity |
| Chemical Composition | Ag |
| Crystal System | Isometric |
| Uses | Jewelry, tableware, coins, electronics, photographic films, ornaments |
Silver as a Native Element Mineral
Silver is rarely found as a native element mineral. When found, it is often associated with quartz, gold, copper, sulfides of other metals, arsenides of other metals, and other silver minerals. Unlike gold, it is rarely found in significant amounts in placer deposits.
Native silver is sometimes found in the oxidized zones above the ores of other metals. It persists there because silver does not readily react with oxygen or water. It does react with hydrogen sulfide to produce a tarnished surface that is composed of the silver sulfide mineral known as acanthite. Many specimens of native silver that have been exposed to the atmosphere or to hydrothermal activity have an acanthite coating.
Most native silver is found associated with hydrothermal activity. In these areas it often occurs in abundance as vein and cavity fillings. A few of these deposits are large enough and rich enough in native silver to support mining. In most cases, the economic viability of the deposit depends upon the presence of other valuable minerals. The mines are usually underground operations that follow the veins and cavities where the native silver occurs.
Native silver is usually without a characteristic crystal habit. When it forms in the open spaces of pockets and fractures, some interesting crystal habits sometimes develop. The crystals are rarely the cubes, octahedrons, and dodecahedrons expected of an isometric mineral. Instead the silver's habit is usually thin flakes, plates, and dendritic crystal clusters formed in the narrow spaces of joints and fractures. Filiform and wire-like habits are also seen.
Minerals that Contain Silver |
|
| Acanthite | Ag2S |
| Aguilarite | Ag4SeS |
| Allargentum | Ag1-xSbx |
| Andorite | PbAgSb3S6 |
| Arcubisite | Ag6CuBiS4 |
| Argentite | Ag2S (when above 177°C) |
| Argyrodite | Ag8GeS6 |
| Arquerite | (Ag,Hg) |
| Berryite | Pb3(Ag,Cu)5Bi7Si6 |
| Boleite | KPb26Ag9Cu24(OH)48Cl62 |
| Bromargyrite | AgBr |
| Canfieldite | Ag8SnS6 |
| Chlorargyrite | AgCl |
| Chrisstanleyite | Ag2Pd3Se4 |
| Crookesite | Cu7(Tl,Ag)Se4 |
| Dyscrasite | Ag3Sb |
| Empressite | AgTe |
| Fettelite | Ag16HgAs4S15 |
| Freibergite | (Ag,Cu,Fe)12(Sb,As)4S13 |
| Freieslebenite | AgPbSbS3 |
| Gabrielite | Tl6Ag3Cu6(As,Sb)9S21 |
| Hessite | Ag2Te |
| Iodargyrite | AgI |
| Jalpaite | Ag3CuS2 |
| Krennerite | (Au0.8,Ag0.2)Te2 |
| Marrite | PbAgAsS3 |
| Miargyrite | AgSbS2 |
| Moschellandsbergite | Ag2Hg3 |
| Pearceite | Cu(Ag,Cu)6Ag9As2S11 |
| Petzite | Ag3AuTe2 |
| Polybasite | [(Ag,Cu)6(Sb,As)2S7][Ag9CuS4] |
| Proustite | Ag3AsS3 |
| Pyrargyrite | Ag3SbS3 |
| Samsonite | Ag4MnSb2S6 |
| Stephanite | Ag5SbS4 |
| Stromeyerite | AgCuS |
| Stützite | Ag5-xTe3 (with x = 0.24 to 0.36) or Ag7Te4- |
| Sylvanite | (Ag,Au)Te2 |
| Uytenbogaardtite | Ag3AuS2 |
Minerals that Contain Silver
The number of minerals that contain silver as an essential constituent is surprising. The green table on this page contains a partial list of silver minerals that includes 39 different species. Each of these is a distinct silver mineral. All of them are rare, but a few (such as acanthite, proustite, and pyrargyrite) can be found in sufficient quantities to warrant mining. Silver minerals can be sulfides, tellurides, halides, sulfates, sulfosalts, silicates, borates, chlorates, iodates, bromates, carbonates, nitrates, oxides, and hydroxides.

Silver copper nugget: A stream-rounded nugget of silver and copper found in Keweenaw County, Michigan. Specimen is approximately 2.7 x 2.1 x 1.3 centimeters in size. Specimen and photo by Arkenstone / www.iRocks.com.
Natural Silver Alloys and Amalgams
Most gold found in placer deposits is alloyed with small amounts of silver. If the ratio between gold and silver reaches at least 20% silver, the material is called "electrum." Electrum is the name for an alloy of gold and silver. A significant amount of today's silver production is a refining byproduct of gold mining.
Silver also forms a natural alloy with mercury. This silver amalgam is sometimes found in the oxidation zones of silver deposits and is occasionally associated with cinnabar.
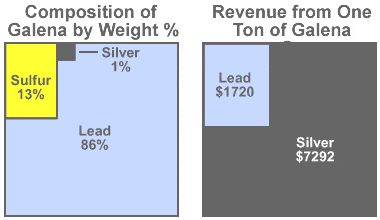
Galena value: Some mines producing galena produce more revenue from the silver content of their ore than from the lead content. Assume that we have a mine that produces argentiferous galena with an average composition of 86% lead, 13% sulfur, and just 1% silver (as shown in the diagram on the left).
If the silver price is $25 per troy ounce and the lead price is $1 per avoirdupois pound, the value of the lead in one ton of ore will be $1720, while the value of the silver in that same ton of ore will be $7292 (as shown in the diagram on the right).
The small amount of silver has a huge impact on revenue because at the prices assumed, silver is 364 times more valuable than an equal weight of lead. It is easy to understand why mining companies get excited by argentiferous galena! Even though galena is the ore being removed and lead makes up the bulk of the product, these mines are often called "silver mines."
Silver as a Constituent in Other Metals and Ores
Most of the silver produced today is a byproduct of mining copper, lead, and zinc. The silver occurs within the ores of these metals in one of two ways: 1) substituting for one of the metal ions within the ore mineral's atomic structure; or, 2) occurring as an inclusion of native silver or a silver mineral within the ore mineral. The value of this minor silver within the ore mineral can exceed the value of the primary metal within the ore.
The accompanying diagram considers the situation of argentiferous galena (galena that contains up to a few percent by weight of silver substituting for lead in the galena mineral structure).

The best way to learn about minerals is to study with a collection of small specimens that you can handle, examine, and observe their properties. Inexpensive mineral collections are available in the Geology.com Store. Image copyright iStockphoto / Anna Usova.
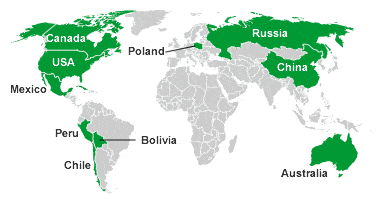
Map of silver-producing countries: The map above shows the top ten silver-producing countries in the world for calendar year 2013. Data from the USGS Mineral Commodity Summary.
Geographic Distribution of Silver Production
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Silver and silver-bearing minerals tend to be closely associated with magmatic activity, as that is where hydrothermal activity also occurs.
This association holds especially well along western North, Central, and South America, where silver production follows the trend of the Andes Mountain Range. Argentina, Bolivia, Canada, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Peru, and the United States are all significant producers of silver today and in the past. In other parts of the world, silver production is associated with igneous activity of any geologic age.
In Europe there is a band of current and geologically ancient volcanic activity that passes from Spain in the west into Turkey in the east. Much of the European silver production has been from this trend.
The table and map above show the top ten silver-producing countries in the world during calendar year 2013.
| More Minerals |
 |
Herkimer Diamonds |
 |
The Acid Test |
 |
Tumbled Stones |
 |
Zircon |
 |
Fool*s Gold |
 |
Kyanite |
 |
Rock Tumblers |
 |
Rhodochrosite |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|
