Geological Terms Beginning With "J"
For terms beginning with other letters, please click below
|

Jade
"Jade" is a cultural term used for a translucent gem material consisting of either jadeite or nephrite. The typical color cut into gemstones and used in ornamental work is a bright to deep green. However, jade can be white, pink, purple, gray, black, or other colors. Jade is a durable stone, well suited for use in jewelry. During ancient human history, jade's durability made it the material of choice for tools and weapons that were used for cutting and impact. It could be fashioned into sharp tools and had a very high resistance to breakage (also known as "toughness").

Jadeite
A high-pressure clinopyroxene that is frequently carved and polished as a gemstone. Jadeite, along with nephrite, are the two minerals that share the cultural term "jade." Jadeite is the more desirable of the two minerals because it is more durable, works easier, and polishes to a higher luster. The photo shows a hand-made Mayan jadeite pectoral from the Mayan Classic period. It was taken by John Hill and distributed by a GNU Free Documentation License.

Jaspagate
A variety of chalcedony that displays characteristics of both jasper and agate. It has both opaque areas and translucent areas.

Jasper
Jasper is an opaque variety of chalcedony that often exhibits interesting patterns and colors caused by impurity inclusions. Jasper differs from agate in that agate is typically translucent and banded, or translucent with visible inclusions that form plume-, moss-, or flame-shaped patterns. Jasper is typically red, brown, orange, yellow, gray, or green and is often associated with iron ores. High-quality specimens of jasper can be polished to a very high luster and are often cut into cabochons or beads for use in jewelry. Jasper is also used to produce tumbled stones and a variety of lapidary products. Shown in the photo are two cabochons of Wild Horse Jasper, one of the many gemstones found in Oregon.
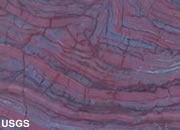
Jaspilite
A sedimentary rock that is made up of alternating bands of red jasper and hematite. It is sometimes rich enough in iron to serve as an iron ore and is occasionally cut into gemstones or used as an ornamental stone.

Jet
Jet is a rock similar to coal with a uniform texture that can be cut into attractive gems. It was popular in Victorian England, where it was used in mourning jewelry. It has a very low specific gravity, which makes a strand of beads, a pair of earrings, or a brooch much lighter than expected. Jet is very soft, so it must be used in jewelry that is not subject to impact or abuse.

Jetty
A human-made structure built at right angles to a coastline and extending into the body of water. Jetties are built to protect an area of shoreline from the effects of currents, erosion, or deposition. Two jetties in the photo protect the entrance to a navigational channel. Note the sediment accumulated behind the jetty on the left side of the channel. Without the jetty, that sediment would have blocked the opening to the channel.

Joint
A planar fracture in rock along which there has been no displacement. Most rock units exposed at Earth's surface have sets of near-vertical, parallel joints that formed in response to unloading or tectonic activity. The photo shows a set of parallel joints in dolomite of the Silurian Sugar Run Formation near Chicago, Illinois.

Joint Set
A group of joints that are parallel or nearly parallel. They are frequently formed at the same time interval from a local or regional unloading event or tectonic activity. The photo shows a set of parallel joints in dolomite of the Silurian Sugar Run Formation near Chicago, Illinois.
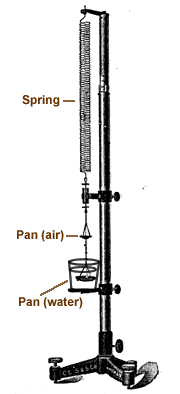
Jolly Balance
A spring balance used in a mineralogy lab for the determination of specific gravity. It consists of long delicate spring with two pans suspended at the bottom. The bottom pan is suspended in a beaker of water.
The object to be tested is placed on the top pan and the linear distance that the spring lengthens is measured. The object is then placed on the bottom pan, completely under water. The amount of spring lengthening is measured again. The lengthening in water is less than the lengthening in air because of the buoyancy provided by the water.
Specific gravity is determined by comparing the lengthening of the spring when the object is on the air pan to the lengthening that occurs when the object is on the water pan, by the following formula.
For example: the specific gravity of gold is 19.3 and the specific gravity of quartz is 2.65.

Junkite
Ugly rocks that some people try to make pretty by processing them in a rock tumbler. Unfortunately, if you want pretty rocks out of a rock tumbler, you have to start by putting pretty rocks in. Junkite in = Junkite out.

Juvenile Water
Water that is new to the hydrologic cycle. Brought to Earth's surface through volcanic eruptions.
|
Dictionary of Geological Terms - Only $19.99 All scientific disciplines have an essential vocabulary that students and professionals must understand to learn and communicate effectively. A geology dictionary that is used regularly is one of the most important tools for developing professional competence. A good dictionary should be on the desk of every geologist and within easy reach. This dictionary is compact and inexpensive at only $19.99. More information. |
|
| More General Geology |
 |
Diamonds from Coal? |
 |
What is a Geyser? |
 |
What is the San Andreas Fault? |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
The Doorway to Hell |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Gifts That Rock |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|

