Geological Terms Beginning With "Q"
For terms beginning with other letters, please click below
|
Quadrangle (Quad)
In geometry: a four-sided plane figure such as a square or a rectangle. In geology: an area shown on a standard topographic map sheet published by the United States Geological Survey. The boundaries of the maps are usually lines of longitude and latitude.
Quake
A slang term used in place of the word "earthquake." The word "quake" is normally used for small earthquakes that do not cause damage.

Quarry
A surface mine usually operated to produce crushed stone for the construction industry, such as limestone, granite, sandstone, or trap rock.

Quartz
One of the most abundant minerals in the Earth's crust. Has a chemical composition of SiO2. Quartz is the index mineral for a hardness of seven on the Mohs hardness scale. Occurs in sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. Several gemstones are composed of quartz. These include rose quartz, smoky quartz, amethyst, and others.

Quartz Arenite
A sandstone consisting of at least 95% quartz. They are thought to attain this very high quartz content because they have been "recycled." During the first depositional cycle, they were deposited as impure sands containing quartz, feldspars, micas, and other minerals. Then, in the second cycle, the additional transport and weathering destroyed what remained of the less durable, non-quartz fraction, leaving a nearly pure quartz sand as the residual.

Quartzite
A metamorphic rock formed by the alteration of sandstone by heat, pressure, and chemical activity. The metamorphism often exerts enough pressure to weld the original quartz sand into a polycrystalline mass.

Quartzose
An adjective used in reference to a sedimentary rock that is composed primarily of quartz.
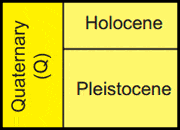
Quaternary Period
The most recent period of geologic time that begins about 2.588 million years ago and extends to the present. It follows the Neogene Period and is divided into the Pleistocene (2.588 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to present).
Quick Clay
Clay-sized particles, often of quartz and feldspar, but sometimes of clay, that lose their strength, collapse, and behave like a fluid when disturbed by vibrations or placed under load. They are mostly found in glaciated areas of the northern hemisphere. Quick clays are often involved with landslides, and they are often the material of failure in landslides that flow over very gentle slopes.

Quicksand
A bed of sand that has a high water content. The water within the sand is often flowing through the spaces between the sand grains. This creates a soft, fluid-like material that yields easily to pressure and in which heavy objects will sink. People and animals have been known to perish in quicksand. Creative commons photo by Ralf Schulze.

Quicksilver
A nickname for the element mercury.
|
Dictionary of Geological Terms - Only $19.99 All scientific disciplines have an essential vocabulary that students and professionals must understand to learn and communicate effectively. A geology dictionary that is used regularly is one of the most important tools for developing professional competence. A good dictionary should be on the desk of every geologist and within easy reach. This dictionary is compact and inexpensive at only $19.99. More information. |
|
| More General Geology |
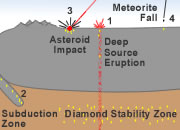 |
Diamonds from Coal? |
 |
What is a Geyser? |
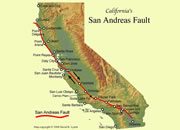 |
What is the San Andreas Fault? |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
The Doorway to Hell |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Gifts That Rock |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|

