Geological Terms Beginning With "R"
For terms beginning with other letters, please click below
|

Radial Drainage
A drainage pattern in which stream channels run away from a central high point such as a volcano or dome. The image show radial drainage on Cerro Culiacan, a volcano in west central Mexico.
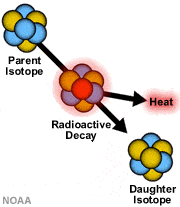
Radioactive Decay
The process through which a radioactive isotope spontaneously transforms into a new substance (the daughter isotope) along with a release of heat.
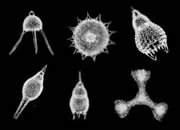
Radiolarians
Microscopic (0.1 to 0.2 millimeter) single-celled marine animals with siliceous skeletons that live in shallow portions of the oceanic water column. Radiolarians have a range from Cambrian to present. They are found as zooplankton in many parts of the world's oceans. When carbon dioxide concentrations are high their siliceous skeletons are soluble

Radiolarian Ooze
A deep-sea pelagic sediment that contains at least 30% siliceous radiolarian remains. The radiolarians live in shallow portions of the oceanic water column, when they die their siliceous skeleton sinks. Where the abundance of radiolarian debris is high enough a radiolarion ooze is found on the seafloor below.

Radiolarite
Radiolarite is a sedimentary rock that forms from the accumulation of microscopic radiolarian tests and is thus of organic origin. Some geologists also consider it to be a mineraloid. The specimen in the photo is from the Windalia Radiolarite, a rock unit that formed on a marine shelf in an area that is now part of the Kennedy Ranges of Western Australia. It can be cut and polished to a high luster and used as a gemstone. It is known in the gem trade as "mookaite."
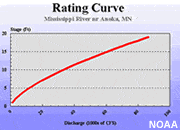
Rating Curve
A plot that shows the relationship between the stage and discharge (streamflow) of a specific stream at a specific location. It is customary to plot stream stage on the y-axis of the plot and discharge on the x-axis. The resulting relationship is normally a curve. Rating curves can be used to estimate discharge (which is time consuming and expensive to measure) using a single stage measurement (which can be collected with automatic equipment). The principle of a rating curve enables hydrologists to monitor the discharge of many streams simultaneously once gages have been placed to collect and report the stage of the stream.
Reaction Series
A series of interactions between a melt and mineral crystals in contact with the melt. In a reaction series the first formed crystals (highest temperature minerals) react with the melt to produce a new mineral.
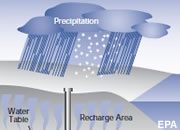
Recharge
The addition of water to an aquifer or other water body. An aquifer is recharged by precipitation in an area where the aquifer has a porous connection to the surface. Precipitation, snow melt and stream infiltration are common methods of recharge.
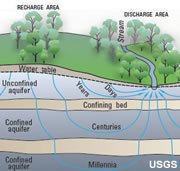
Recharge Area
The geographic area where water infiltrates into the ground and enters an aquifer.
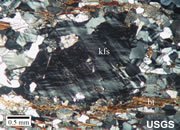
Recrystallization
A solid state reaction in which the atoms of existing crystals within a rock are reorganized in response to heat and/or pressure. The recrystallized mineral grains are typically larger in size than the original crystals. The photomicrograph is of a metamorphic rock in which feldspar grains have been recrystallized, as evidenced by their straight grain contacts.
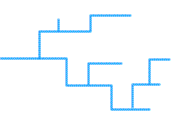
Rectangular Drainage
A drainage pattern in which stream channels develop within a large-scale network of intersecting joints. This drainage pattern is characterized by right-angle bends in the channels of streams and streams that intersect at right angles.
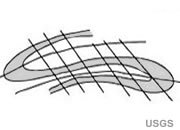
Recumbent Fold
A recumbent fold has an axial surface that is nearly horizontal. One of the limbs will have strata that is overturned.

Redrilled Well
A previously drilled hole that is reentered and deepened by additional drilling. In some shale formations a contractor arrives and drills a vertical well to the kickoff point. Later, another contractor arrives to drill the horizontal leg of the well and frack the well.
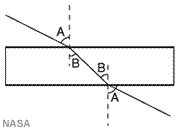
Refraction
The bending of a seismic wave as it enters a material of different density, or, the bending of a beam of light as it enters a material of different refractive index. In the image, a beam of light travelling through air strikes a piece of glass, as the light enters the piece of glass it bends (refracts) towards the denser medium (the glass). As the light exits the glass, it again bends towards the denser medium (the glass). This bending of light is known as "refraction."
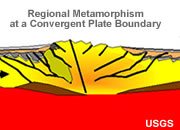
Regional Metamorphism
Metamorphism across a broad geographic area caused by the elevated temperatures and pressures of plate collision or deep burial. This type of metamorphism usually occurs at continental margins.

Regolith
A general term used in reference to unconsolidated rock, alluvium or soil material on top of the bedrock. Regolith may be formed in place or transported in from adjacent lands. The term is used for the surface material of Earth, Moon, Mars and other planets. Shown in the photo is a footprint in lunar regolith from the Apollo 11 mission.
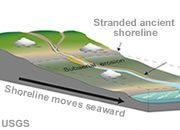
Regression
A retreat of the sea from land areas. Possible causes include a drop in sea level or uplift. In response, the shoreline moves seaward, exposing the coastal plain to erosion.

Relief
Variations in the height and slope of Earth's surface. Also used in reference to the vertical difference between the highest and lowest elevations of an area. The image is a small relief map of the Appalachian, Blue Ridge and coastal plain portions of Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland and Delaware.

Remote Sensing
The collection of information about an object or area from a distance, frequently using data obtained from satellites, aircraft or underwater vehicles. Some of the many methods employed include: photography, radar, spectroscopy and magnetism.

Replacement
The dissolving or disintegration of one material followed by precipitation of a new material in its place. Often an important step in the fossilization process. The photo shows logs of petrified wood from the Chinle Formation of Arizona. The cell walls in the wood were replaced and infilled by chalcedony.
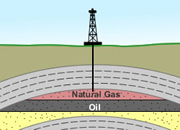
Reservoir
A subsurface rock unit that is porous and permeable, and that contains an accumulation of oil and/or natural gas. The image shows an anticline serving as a reservoir structure for oil and natural gas.
Retrograde Metamorphism
Mineral changes within a rock that are caused by adjustments to conditions of reduced temperature and pressure.
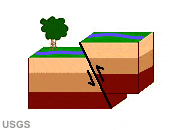
Reverse Fault
A fault with vertical movement and an inclined fault plane. The block above the fault has moved upwards relative to the block below the fault. Reverse faults are the typical structural style of convergent plate boundaries and portions of the crust that are under compression. Also known as a "thrust fault."

Rhodolite Garnet
Rhodolite is a purplish red to violet-red variety of garnet that is a combination of pyrope and almandine. It often has wonderful color and clarity at a relatively low cost - and that is helping it become popular in jewelry.

Rhodochrosite
Rhodochrosite is a manganese carbonate mineral that is popular because of its beautiful pink color. It is typically has lacy or concentric bands. Its softness limits its use to earrings, pendants, pins and other low-abrasion items.

Rhodonite
Rhodonite is a manganese mineral that sometimes occurs in a very attractive pink color. Usually translucent-to-opaque, it is a popular gem material. Rarely, it is transparent and used for faceting.

Rhyolite
The fine-grained volcanic or extrusive rocks that are equivalent in composition to granite. Normally white, pink or gray in color.
Richter Magnitude Scale
A scale that is used to compare the strength of earthquakes based upon the amount of energy released. The scale is logarithmic and an arbitrary earthquake was used as a starting point for creating the scale. As a result it is a continuous scale with no upper limit and negative numbers possible for very small earthquakes. An upper limit of approximately 9.0 is suspected as Earth materials will most likely fail before storing enough energy for a larger magnitude earthquake.
Ridge (Mid-Ocean)
An elevated area of the sea floor in the center of an ocean basin with rugged topography, a central rift-valley and recurring seismic activity. Ridges generally stand about 1000 meters to 3000 meters above the adjacent ocean floor and are about 1500 kilometers in width.
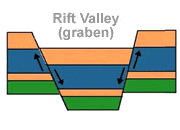
Rift Valley
A valley bounded by normal faults that has formed in an area of crustal extension such as a divergent plate boundary. The East Africa Rift is the world's most famous example of an area with rift valleys.
Right-Lateral Fault
A fault with horizontal movement. If you are standing on one side of the fault and look across it, the block on the opposite side of the fault has moved to the right. (Also see Left-Lateral Fault.)
Rip Current
A strong, narrow current of high velocity and short duration that flows seaward through the breaker zone. Caused when a buildup of water pushed onto the beach by winds and waves returns seaward.
Ripple Marks
A series of parallel or sub-parallel ridges in sand or sediment that is caused by the rhythmic or directional movement of wind or water.
|
Dictionary of Geological Terms - Only $19.99 All scientific disciplines have an essential vocabulary that students and professionals must understand to learn and communicate effectively. A geology dictionary that is used regularly is one of the most important tools for developing professional competence. A good dictionary should be on the desk of every geologist and within easy reach. This dictionary is compact and inexpensive at only $19.99. More information. |
Rock Cycle
All rock at or near Earth's surface is being modified by the processes of metamorphism, melting, crystallization, lithification and weathering. These processes move rock material through the states of metamorphic rock, igneous rock, sedimentary rock, melts and sediment. The natural and continuous cycling of rock materials through these states is known as the rock cycle.
Rock Flour
Finely pulverized rock material of silt or smaller size produced by abrasion at the base of a glacier.

Rock Glacier
A mass of rock material, cemented together by ice, that flows down a slope under the force of gravity much like the motion of an ice glacier. Rock glaciers often head in a cirque and may have no visible ice at the surface. Most often seen in the same parts of the world where ice glaciers are abundant. The image is a view of a rock glacier near McCarthy, Alaska by the National Park Service, Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve.

Rock Salt
A chemical sedimentary rock that forms from the evaporation of ocean or saline lake waters. It is also known by the mineral name "halite." It is rarely found at Earth's surface, except in areas of very arid climate. It is often mined for use in the chemical industry or for use as a winter highway treatment. Some halite is processed for use as a seasoning for food.

Rock Tumbler
A machine used to smooth and polish rocks. They are a popular tool used by jewelry, craft and lapidary hobbyists in the production of tumble-polished stones.

Rockfall
A sudden downward movement of rock from a steep slope or cliff. The falling rock might have separated from the outcrop along fractures, joints or bedding planes. Movement occurs by free-fall, bouncing or rolling. Falls are often triggered by interstitial ice or water. Shown in the photo is a large rockfall in Yosemite National Park photographed by Herb Dunn.
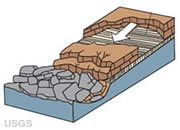
Rockslide
A type of mass wasting in which rock debris detaches and slides down a slope under the influence of gravity. The movement usually occurs over a planar surface such as a bedding plane, joint surface or fault plane. The moving mass can break apart during transport or remain in a large mass.

Roiled
Water that has been disturbed and is carrying suspended material, reducing its clarity. The word is often used in reference to lake water that has been muddied by a stream carrying in a load of suspended sediment. Also known as "turbid." The photo shows a heavy plume of suspected sediment entering Lake Tuscaloosa in Alabama.
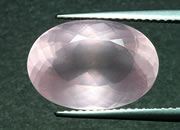
Rose Quartz
Rose quartz is a translucent-to-transparent variety of quartz with a light to deep pink color. It is a gem material that is very common in nature. It is usually cut into cabs and occasionally faceted.
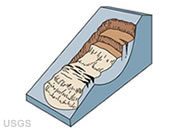
Rotational Slide
Also known as a "slump." A slide in which the surface of rupture, or slip plane, is curved concave upward and the slide movement is roughly rotational instead of translational.

Roughneck
Roughneck is a slang term for an oil field worker who does hard manual labor on the floor of a drilling rig. Much of their work is the repetitive manipulation of drill pipe as the well is being drilled and when all of the pipe must be pulled to change the bit. They do any other work as required to keep the drilling progress moving. They must be strong, physically fit enough to work long hours, willing to get extremely greasy and dirty, and work outdoors in all types of weather throughout the year.

Roustabout
Roustabout is oil field slang for a person who does any low-skill job needed at a drilling site. This work might include equipment maintenance, mowing, painting, errands, cleaning, and whatever is needed to keep the rig operating and the drilling moving forward. All of this is done outdoors, in all types of weather, throughout the year. The roustabout might occasionally work on the drilling floor with the roughnecks and move up to the position of roughneck if skill and physical abilities allow.


Ruby in Fuchsite
Fuchsite is a metamorphic mica with a green color that often contains bright red corundum crystals or "rubies." It is often carved and cut into cabochons. Frequently confused with "ruby in zoisite."

Ruby in Zoisite
Ruby in zoisite is an interesting material. Massive green zoisite often contains bright red ruby crystals. The color combination makes an attractive and unique gem material. It is often cut and carved into small sculptures.

Runoff
Liquid water moving over the land surface as a sheet or channelized flow. The portion of precipitation that moves over the ground instead of evaporating or infiltrating.

Rupture Strength
The maximum amount of stress that a brittle material can sustain without failure.

Rutilated Quartz
Rare specimens of clear quartz have needle-shaped inclusions of rutile. These can be used to cut interesting and attractive cabochons and faceted stones.
|
| More General Geology |
 |
Diamonds from Coal? |
 |
What is a Geyser? |
 |
What is the San Andreas Fault? |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
The Doorway to Hell |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Gifts That Rock |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|

