Andalusite: Andalusite is a strongly pleochroic gem. "Pleochroic" means that it can display different colors when viewed from different directions. Expert cutters working with excellent specimens can produce faceted stones that display both of a specimen's pleochroic colors in the face-up position. Photographs and specimens by glorious85.
What is Andalusite?
Andalusite is an aluminosilicate mineral with a chemical composition of Al2SiO5. It forms at low to medium metamorphic temperatures and pressures where argillaceous rocks (such as shale) are exposed to regional and contact metamorphism.
Andalusite is a rock-forming mineral most commonly found in schist, gneiss, and hornfels. Minor amounts are also found in granite and granitic pegmatite.
The most important use of andalusite is in making heat-resistant bricks and ceramic objects used in the steel-making and metal processing industries. It is also used to make chemicals, glass and a variety of ceramic products. Exceptional crystals of andalusite are valued by mineral collectors. Specimens with spectacular color and clarity are cut into gemstones.

Chiastolite: A cabochon cut from a specimen of the chiastolite variety of andalusite. This specimen exhibits a sharp cross, formed from graphite particles that were pushed out of the way during crystal growth. The diagonal fiber of this specimen is a result of needle-like crystals (possibly rutile crystals) that have grown within the andalusite crystal.
What is Chiastolite?
Chiastolite is a variety of andalusite that contains black particles of graphite arranged in geometric patterns. The graphite is pushed aside by crystal growth within a rock that is being metamorphosed. As growth occurs, the particles become concentrated at crystal interfaces. The result can be a cross-shaped pattern within the mineral - similar to the "cross-stone" shown in the accompanying photo.
People have known about these cross stones for centuries and have valued them for their perceived religious or spiritual meaning. Attractive specimens are often cut and polished for use as amulets, charms, and novelty gems.

Twinned andalusite crystals: Twinned crystals of andalusite (chiastolite) in a piece of black micaceous schist. Photo by Moha112100, displayed here under a Creative Commons license.
Physical Properties of Andalusite | |
| Category | Silicate mineral |
| Chemical Composition | Al2SiO5 |
| Crystal System | Orthorhombic |
| Color | Greenish brown, yellowish green, pinkish brown, orangy brown, white, gray. Strongly pleochroic, often with yellowish green and orangy brown colors. |
| Streak | White |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Diaphaneity | Transparent to nearly opaque |
| Cleavage | Poor to good in one direction |
| Fracture | Uneven to conchoidal with vitreous fracture luster |
| Tenacity | Brittle |
| Mohs Hardness | 6.5 to 7.5 |
| Specific Gravity | 3.17 |
| Crystal Habit | Usually massive. Crystals are prismatic with a nearly square cross section, sometimes in columnar aggregates. |
| Refractive Index | 1.630 to 1.643 |
| Diagnostic Properties | Strongly pleochroic. Prismatic crystals with a nearly square cross-section. Associated with kyanite, sillimanite, corundum, or cordierite. |
| Uses | Used to make heat-resistant bricks and ceramic objects used in the steel-making and metal processing industries. Used to make chemicals, glass and ceramic products. Specimens with exceptional clarity and color are cut into gems. |
Physical Properties and Uses of Andalusite
Andalusite has a number of useful physical properties. It has the ability to withstand high temperatures without alteration. For that reason it is used to make high-temperature ceramics and refractories. The white porcelain of some spark plugs is made using andalusite.
Andalusite is one of a small number of minerals that commonly forms prismatic crystals with a square cross-section (see accompanying photo). This can be important information for identification in the field.
Transparent specimens of andalusite are often strongly pleochroic. This makes them have different apparent colors when viewed from different directions. This pleochroic effect allows andalusite to be cut into unique gemstones.
Although twinning is not common in andalusite, nicely crystallized specimens that possess twinning can be distinctive. Twinning can produce cross-shaped structures perpendicular to the crystallographic c-axis, similar to what is shown in the rock in the accompanying photo above.
How Does Andalusite Form?
Andalusite forms during the regional metamorphism of shale. It is found in schist and gneiss at some present and ancient convergent plate boundaries where the rocks have been exposed to the temperatures and pressures needed for its formation. In these rocks, andalusite is often associated with kyanite and sillimanite.
Andalusite also forms during the contact metamorphism of shale. In this situation, it can form within the metamorphosed rock or in veins and cavities of the igneous rock causing the metamorphism. It can be associated with cordierite in hornfels, granite, and granitic pegmatite.

Andalusite: Crystals of andalusite showing their prismatic habit and square cross-section. These crystals are from Lisens Valley, Austria. Specimen and photo by Arkenstone / www.iRocks.com.

The best way to learn about minerals is to study with a collection of small specimens that you can handle, examine, and observe their properties. Inexpensive mineral collections are available in the Geology.com Store. Image copyright iStockphoto / Anna Usova.

Andalusite: A scatter of faceted andalusite. If you look closely at these gems, you can see that many of them appear to be composed of a mosaic of color. This is an expression of the strong pleochroism of andalusite. Image by cobalt123, displayed here under a Creative Commons license.
Andalusite: An Indicator Mineral
|
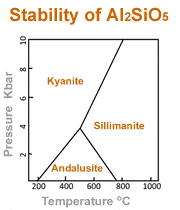
Andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite all share the chemical composition of Al2SiO5. However, they have different crystal structures. Their crystal structure differs because they form under extremely different conditions of temperature and pressure. The phase diagram at left summarizes the conditions under which these minerals form.
Andalusite is the low-temperature mineral of the three. Sillimanite is the high-temperature mineral, and kyanite forms at high pressures and lower temperatures.
Information from a phase diagram can be useful during mineral exploration. If a geologist finds andalusite in the field, the phase diagram reveals the possible range of temperatures and pressures that the rocks were subjected to when the andalusite crystallized.
If the mineral being sought has a dramatically different temperature and pressure of crystallization, then it might not be present in those rocks. If the pressure range of the target mineral is higher, then it is possible that it exists at depth. If the temperature range of the target mineral is higher, then exploration should move toward a heat source or toward greater depth. That is a simplified example of how the phase diagram can be used.
| More Minerals |
 |
Herkimer Diamonds |
 |
The Acid Test |
 |
Tumbled Stones |
 |
Zircon |
 |
Fool*s Gold |
 |
Kyanite |
 |
Rock Tumblers |
 |
Rhodochrosite |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|