Geological Terms Beginning With "L"
For terms beginning with other letters, please click below
|

Labradorescence
A display of spectral colors caused when light enters a material, strikes twinning or other planar surfaces within the stone and then reflects from them. Different twinning surfaces within the stone can reflect different colors of light to produce the visual effect of a stone with different color domains. This phenomenon is best known in the mineral labradorite, for which it is named. Highly labradorescent specimens of labradorite are given the trade name of "spectrolite" for their bold spectral colors.

Labradorite
A gemstone variety of plagioclase feldspar that produces flashes of iridescent blue, green, yellow, orange, or red when moved under incident light. This luster is known as labradorescence.
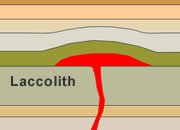
Laccolith
An igneous intrusion that has been forced between two layered sedimentary rock units. The pressure of the injecting magma was high enough to deform the overlying strata. The roof of the intrusion is convex upwards and the floor of the intrusion is nearly flat.

Lacustrine
The word "lacustrine" means "of a lake." In geology the word is used for the depositional environment or a habitat that is found in lakes. Lacustrine environments are usually, but not always, fresh water. They are also usually, but not always low energy. The USGS image shows scientists sampling glacial lake clays associated with landslide problems at Tulley Valley, New York.

Lahar
A mudflow composed of water and volcanic ash. Lahars can be triggered by the flash melting of the snow cap of a volcanic mountain or by heavy rain. Lahars are very dangerous because they can occur suddenly and travel at great speeds. They can travel faster than the streams in the valleys that they pass through, sweeping up stream water, sediment and other debris, and growing in mass as they flow. The photo shows a lahar exiting the crater of Mount St. Helens in 1982. The lahar flowed down the mountain, entered the North Fork Toutle River valley and eventually entered the Cowlitz River about 50 miles downstream.
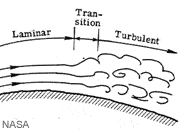
Laminar Flow
A state of uniform flow within a fluid in which the moving particles travel along parallel paths (compare with Turbulent Flow).
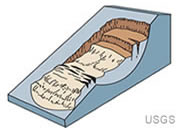
Landslide
The movement of rock, soil, volcanic ash or other material, downslope under the influence of gravity. There are many types of landslides that include: slumps, creep, earthflows, debris flows, debris avalanches, topples, rock falls, mudflows, and debris slides are examples. Landslides are often triggered by rain fall, snow melt, overloading or earthquakes.

Lapilli
Volcanic rock materials which are formed when magma is ejected by a volcano. Typically used for tephra that ranges between 2 and 64 millimeters in diameter.

Larimar
Larimar is a rare blue variety of pectolite found only in the Dominican Republic. It is popular because of its delicate blue color. It must be used with care because it is fragile and will fade with long exposure to bright light.
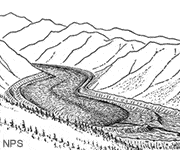
Lateral Moraine
An accumulation of rock debris along the sides of a glacier in contact with the valley walls. It is mainly weathering debris that fell from the valley wall rather than material moved by and deposited by ice.

Lava
Molten rock that has erupted onto Earth's surface. The word is also used for the solidified flows and fragments after they have cooled. The image shows a pahoehoe flow on Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii. Not to be confused with "magma," which is the same material while it is beneath Earth's surface.

Lava Channel
Pathways of lava movement across the surface of a volcano. They can be straight or meandering depending upon the steepness of slope and the obstacles. The photo is a lava channel on the surface of Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii in 1990.

Lava Dome
A round, steep-sided extrusion of very viscous lava that is slowly squeezed from a volcanic vent without major eruption. The lava is too viscous to flow and is composed of rhyolite or dacite. The dome shown in the photo is the vent of the Novarupta eruption of 1912, the largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century. The small dome was overlooked when the source of the eruption was originally determined and the wrong volcano was blamed. Also called "volcanic dome" or "dome volcano".

Lava Flow
An outpouring of molten rock onto Earth's surface, either from a volcanic cone or from a volcanic fissure. The name "lava flow" is used for the erupted material in either the molten state or in the solid state after the molten lava cools and solidifies.

Lava Tube
When the surface of a lava flow solidifies but the lava keeps flowing below, a tunnel can remain after all of the lava drains away. The photo shows an opening into a lava tube at the Lava Beds National Monument in California.
Leaching
The removal of soluble constituents from a rock or soil by moving groundwater or hydrothermal fluids.
Lease Bonus
Money paid to a mineral rights owner in exchange for granting a lease. This payment may be in addition to any rental or royalty payments.
Left-Lateral Fault
A fault with horizontal movement. If you are standing on one side of the fault and look across it the block on the opposite side of the fault has moved to the left. (Also see Right-Lateral Fault.)

Lepidolite
A lithium-rich mica with a rose to lilac color and an aventurescent luster that is sometimes used to make cabochons, tumbled stones and other lapidary projects.

Levee
A long continuous ridge built by people along the banks of a stream to contain the water during times of high flow.
Limb
One side of a fold. The dipping rock units between the crest of an anticline and the trough of a syncline.

Limestone
A sedimentary rock consisting of at least 50% calcium carbonate (CaCO2) by weight. Picture of Limestone.
Lineament
A straight topographic feature of regional extent which is thought to represent crustal structure. A fault, line of sinkholes, straight stream stretch or a line of volcanoes can be considered linear features.

Liquefaction
Liquefaction occurs in unconsolidated sediments that often have pore spaces filled with water. A sudden shock or vibration, produced by an event such as an earthquake, can mobilize the sediment with a loss of grain-to-grain frictional contacts. This causes the sediment to lose strength and fail by compaction, subsidence, or downslope flow. On a subaqueous slope, the failure can result in a subaqueous slump or in severe situations a turbidity current. In the photo, a loss of foundation strength caused by liquefaction caused the buildings' foundations to settle.
|
Dictionary of Geological Terms - Only $19.99 All scientific disciplines have an essential vocabulary that students and professionals must understand to learn and communicate effectively. A geology dictionary that is used regularly is one of the most important tools for developing professional competence. A good dictionary should be on the desk of every geologist and within easy reach. This dictionary is compact and inexpensive at only $19.99. More information. |

Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Natural gas that has been converted to the liquid state by reducing its temperature. (At standard surface temperature and pressure, the liquification temperature is about -260 degrees Fahrenheit.) Liquification will reduce 610 cubic feet of natural gas into a single cubic foot of LNG. LNG provides a convenient and efficient way to transport natural gas from one port to another where pipelines are not available. Image copyright iStockphoto / Mayumi Terao.
Lithification
The processes through which sediments are converted into sedimentary rock, including compaction and cementation.
Lithology
The study and description of rocks, including their mineral composition and texture. Also used in reference to the compositional and textural characteristics of a rock.
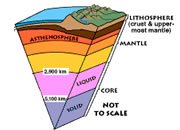
Lithosphere
The rigid outer shell of the earth which includes the crust and a portion of the upper mantle.
Lithospheric Plate
A large slab of the lithosphere that can be moved by convection current motion within the mantle.
Load
The total amount of sediment being carried by a stream or a glacier. Includes suspended materials, dissolved materials and materials moved along Earth's surface. (Also see: bed load, dissolved load, suspended load.)
Lode
A rich accumulation of minerals in solid rock. Frequently in the form of a vein, layer or an area with a large concentration of disseminated particles. (See placer deposit for contrast.)
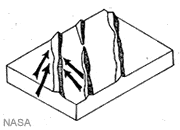
Longitudinal Dune
A long, narrow sand dune that has its long dimension oriented parallel to the direction of the wind. It moves in the same direction as the wind.
Longitudinal Profile
A cross section of a stream or valley beginning at the source and continuing to the mouth. These profiles are drawn to illustrate the gradient of the stream.
Longshore Current
A flow of water parallel to a coastline that is caused by waves striking the coast at an oblique angle.
Longshore Drift
The movement of sediment along a coastline caused by waves striking the coast at an oblique angle. The waves wash sediment particles up the beach at an oblique angle and the swash back to the sea carries the particles down the gradient of the beach. This produces a zig-zag path of particle movement along the beach.
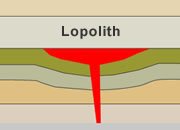
Lopolith
An igneous intrusion that has been forced between two layered rock units. The floor of the intrusion is convex downwards and the roof of the intrusion is nearly flat.
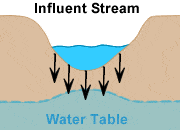
Losing Stream
Also known as an "influent stream." A stream, usually flowing in an arid area, that loses water into the ground through the bottom of its channel. This loss occurs because the water table is below the channel of the stream. Influent streams decrease in discharge in a downstream direction and often lose all of their water into the ground.
Lowland
A relatively flat area in the lower levels of regional elevation.
Low-Velocity Zone
A zone within the upper mantle where seismic wave velocities are relatively low. This zone is located about 35 to 155 miles below the surface.

Luster
The manner in which light reflects from the surface of a mineral. Metallic, submetallic and non-metallic are the basic types of luster. Other types of luster include: vitreous, dull, resinous, adamantine, earthy, pearly, greasy, silky, and waxy. The intensity of luster is often described in simple terms such as bright or dull. In the photo are specimens of tumble-polished hematite with a bright metallic luster.
|
| More General Geology |
 |
Diamonds from Coal? |
 |
What is a Geyser? |
 |
What is the San Andreas Fault? |
 |
Igneous and Volcanic Features |
 |
The Doorway to Hell |
 |
Topo Maps |
 |
Geology Dictionary |
 |
Gifts That Rock |

Find Other Topics on Geology.com:

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

| ||

|

|

